Nothing worries someone more than finding a lump where there shouldn’t be one. A common example are thyroid nodules/ lumps that occur in the neck. But what exactly are thyroid nodules? Are thyroid nodules cancerous? When should thyroid nodules be a concern? And what are the warning signs of thyroid cancer you should look out for?
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are thyroid Nodules?
The thyroid gland is responsible for the production of the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which play important roles in controlling body temperature, metabolism, heart rate, mood, and digestion.
Thyroid nodules, also known as neck lumps, are an abnormal growth that occur in the thyroid gland.
Thankfully, in most cases, thyroid nodules are non-cancerous (i.e. benign nodules).
Thyroid nodules may comprise blood, pus, other fluids, and/or even solid tissues. Thyroid nodules may appear as a single growth or in clusters and they vary in size.
For smaller nodules, they are usually not detectable and are often discovered during routine medical check-ups.
Some nodules, however can grow to a point where they appear as enlarged thyroid gland/goiter and they may compress the air passage and cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing and result in hoarse voice.
In rare cases, thyroid nodules may produce excessive thyroxine (a hormone produced by thyroid gland) which can lead to a condition of overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) with the following symptoms:-
- Muscle weakness
- Unintentional weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heart rate
- Sleeplessness
- Hair loss
- Shakiness or trembling
- Diarrhoea
What are the warning signs of thyroid cancer?
While most thyroid nodules are benign or non-cancerous, you can never be 100% sure that your thyroid nodule isn’t cancerous, without proper screening.
If you notice the following symptoms in conjunction with a thyroid nodule, you may want to get a screening done to ensure that they are not malignant:
- Pain or discomfort associated with the nodule
- Hoarseness or other voice changes
- Persistent cough
- Breathlessness
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing
- Lumps at the side of your neck (enlarged lymph nodes)
What causes thyroid nodules?
The main cause of thyroid nodules are usually unknown, however, the following have been linked to thyroid nodules:
- Genetics: thyroid nodules may run in families
- Iodine deficiency: a diet Low in iodine can cause your thyroid gland to produce nodules.
Are thyroid Nodules Cancerous?
Thyroid nodules can be either benign or cancerous. To ascertain their nature, medical professionals often use diagnostic tools such as ultrasound and ultrasound-guided biopsy. These imaging techniques help assess the characteristics of the nodules
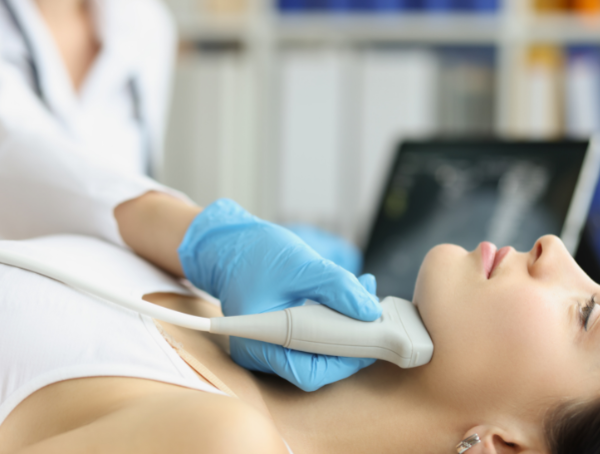
Thyroid Ultrasound
Ultrasounds are the gold standard for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules. It works by sending high frequency sound waves out into the body which then bounce back when it encounters an object, i.e. the thyroid nodule. Not only does an ultrasound detect the mere presence of a thyroid nodule, it can also determine what the thyroid nodule is made of and if it has any cancerous characteristics.
You can expect the following steps during an ultrasound examination:
- Ultrasound gel is applied to your neck.
- Ultrasound wand is used to obtain images of the area.
- If a thyroid nodule is observed, it will be analysed to identify its composition and to check for any characteristics associated with thyroid cancer.
Ultrasound-guided Biopsy
If a cancerous thyroid nodule is suspected, an additional test is carried out. This is known as a fine-needle aspiration, or an ultrasound guided biopsy.
You can expect the following steps during a fine needle aspiration:
- The area is cleaned and sterilised.
- Local anaesthesia is administered at the procedure site.
- A thin sterile needle is inserted (with the assistance of an ultrasound) into the nodule to obtain a sample of cells.
- The samples are sent to a laboratory to check for the presence of cancer cells.
What are the characteristics of cancerous thyroid nodules?
During an ultrasound scan of the thyroid nodule, your doctor will look out for the following characteristics that are associated with thyroid cancer:
- Nodules with ill-defined edges
- Irregular shaped nodules
- Nodule is taller than it is wide
- Hardened tissue within nodule
- Absence of elasticity
If your doctor has noticed any of the above characteristics in your thyroid nodule, further tests will be conducted to confirm diagnosis.
What should I do if I have cancerous thyroid nodules?
Thyroid cancer is recognized as the 8th most common cancer diagnosed in women in Singapore, as reported by the Singapore Cancer Society.
It can be quite daunting and worrying to be diagnosed with thyroid cancer. Rest assured, our doctors here at the Centre for Screening and Surgery are well-versed in the detection and treatment of cancerous thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer.
If you find yourself in this situation, rest assured that our dedicated team is here to guide you through the process. The treatment for cancerous thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer are dependent on its severity or stage. Let’s take a look at the treatment options available for thyroid cancer.
Endoscopic thyroid surgery
A type of keyhole or laparoscopy surgery, this procedure is scarless and removes a part of or the whole thyroid through a small hole near the thyroid nodule. After general anaesthesia is administered, a thin flexible scope with an attached camera is inserted into the hole and with the guidance of the camera, the necessary parts are removed, and a drainage tube is placed. The hole is sutured up and the drainage tube will be removed a few days post-surgery.
Radioactive iodine treatment
Commonly used as a follow-up treatment after surgery has been conducted to remove part of or the whole thyroid gland. It helps to eradicate any remaining cancer cells and also works to remove cancer cells that have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Radioactive iodine is effective because the thyroid gland absorbs almost all iodine present in the body. Therefore, when radioactive iodine is administered and absorbed by the thyroid gland, the radiation will eradicate all thyroid cells without discrimination and without harming other healthy organs and tissues.
Thyroidectomy or open surgery
This traditional procedure involves the removal of either part of the thyroid, the whole thyroid, and/or nearby lymph nodes. It is an in-patient procedure which means you will have to stay at the hospital for a few days for observation.
During the procedure, you will be placed under general anaesthesia so you will not feel any pain. An incision is made near the thyroid nodule and your doctor will remove the necessary tissue before a drainage tube is inserted. The area is then sutured up. The drainage tube will be removed in the days following the surgery.
In conclusion, the likelihood of a thyroid nodule being cancerous is low but not impossible. And like all types of cancer, early detection and treatment is key to survival. Do not hesitate to make an appointment for screening and consultation with our doctor today.
FAQ
Thyroid nodules are very common, affecting approximately 60% of the population in Singapore.
This depends. If the nodule is benign and not causing any symptoms or problems, they can be left untreated and just monitored. If the nodule is benign but causing problems such as difficulty breathing or swallowing, they need to be removed using either open thyroid surgery or endoscopic thyroid surgery. If the nodule is cancerous, it must be removed whether it is causing problems or not. Cancerous nodules can be removed using open thyroid surgery, endoscopic thyroid surgery and then possibly followed up with radioactive iodine treatment—this depends on the extent of spread if any, what stage your thyroid cancer is at, and how big the thyroid nodule is.
No, if your benign thyroid nodule is not causing you any pain or discomfort, it is not necessary to remove it.
Some thyroid nodules that are fluid-filled can go away on their own but solid thyroid nodules may grow larger even if they are benign.